Knock Knees: Know the causes, symptoms & treatment
Knock knee is commonly known by several names like knock knee deformity, knock knee syndrome, and knocked knee. It is an incorrect alignment of legs that affect people of all ages. If it is not treated on time, it can give knee pain and degenerate the knees. Treatment will correct the deformity and improve knee mechanics and walking capability. Also, the timely treatment can reduce pain and prevent rapid degeneration of the knees.
What is a Knock Knee?
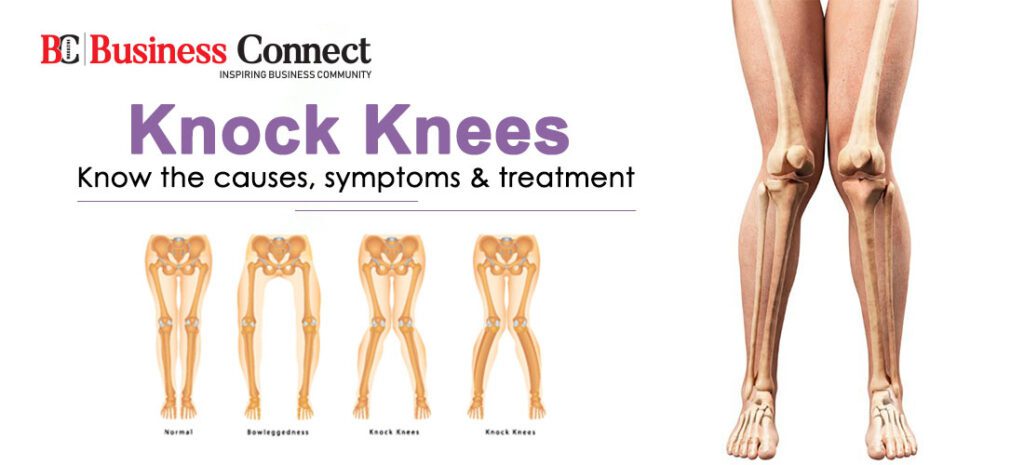
Knock knees is one of the deformities of legs which can be seen easily when a person stands with both the legs together. A person with knock knees has a wide gap between their feet when they stand with their knees together. The knees bend inwards and knock together. This condition occurs generally in young children; however, anyone can experience it.
Knock knees is also known as genu valgum and commonly seen in those adolescents and children who are obese, have flat feet or have hypermobile joints. In many people, knock knees get into the right position on their own but in some, it may indicate an underlying condition like rickets or other bone diseases.
What Causes Knock Knees?
Knock knees are commonly seen in overweight children aged 6-7 and considered a normal part of growth and development. Usually, the legs straighten up with time as the child grows but sometimes mild knock knees condition can last into adulthood. If the condition develops later in childhood and doesn’t go away with age, then it can be a result of some underlying congenital or developmental disease or it arises after an infection or a traumatic knee injury. Common causes of knock knee are as follows:
- Metabolic disease
- Benign bone tumours
- Bone infection
- Physical trauma
- Renal(kidney) failure
- Congenital(inborn) conditions
- Rickets (lack of vitamin D causes it)
- Fractures that heal with a deformity(malunion)
- Growth plate injury
- Arthritis, specifically in the knee
The common Symptoms
An affected person shows separation in his ankles when his knees are positioned together. Other symptoms such as pain are often caused by gait (manner of walking) is experienced by the person affected with knock knees. Symptoms may include:
- Knee instability
- A limp while walking
- Stiff or sore joints
- Foot or ankle pain
- Knee or hip pain
- Progressive knee arthritis in adults
- Reduced range of motion in hips
- Feet not touching while standing with knees together
- Foot or ankle pain
- Difficulty in walking or running
a person might experience any other symptoms from an underlying condition that is causing this deformity. This is seen often in affected people of all age groups that they feel overload on one or both the knees which leads to pain. And the same can cause deformity, knee instability and progressive degeneration of the knee joint. Old age people who have this condition for many years often overload the outside of the knee and stretch the inside. Such shifts of load cause pain, knee instability and arthritis.
Diagnosis of Knock Knee
Orthopaedic doctor examines the patient and sees his family medical history or any pre-existing conditions and current health. The doctor also does a physical examination of the legs and gait (manner of walking). Standing-alignment X-rays are taken to confirm the diagnosis. The diagnosis helps the doctor exact location of deformity.
Prevention
Most cases of knock knees are the results of lack of vitamin D. 90% of the affected children below the age of 8 years have overcome this condition by just taking vitamin D after diagnosing the levels through basic X-rays. Bracing is another solution which repositions the knees. If this doesn’t work and the patient is an adult, a knee alignment osteotomy is done to stop or delay the requirement of knee replacement. In case knee knock is the result of an underlying illness or infection, then the first doctor will treat that condition, after that any orthopaedic correction will begin.
Mild cases of knock knees in children or adolescents may use braces to position the bones to grow in the right angle. In a condition when gradual correction doesn’t work, surgery can be recommended. In children, guided growth minimal-incision surgery can be used to help the leg grow straight. In extreme cases and in skeletally mature adolescents and adults an osteotomy (bone is cut and then aligned) may be needed to straighten the bone. Thighbone-femur- is operated in most such cases. This is called distal femoral osteotomy (DFO). In some patients, tibial osteotomy, in which the tibia shinbone is realigned, is done. Few specific cases may require both femoral and tibial osteotomy.
Must Read:-
- Top 10 Young Entrepreneurs in India 2022
- Upcoming Indian Web Series for 2022-23
- Top 10 Hospitals in India 2022
- Top 10 richest player of the world 2021
- Top 10 highest-paid Indian Athletes 2021
- Top 10 highest paid CEO in the World
- Top 10 richest person of India
- Top 10 Highest Paid CEOs of India
- List Of Most Followed Facebook Pages in 2022
- The Success Story of Jeff Bezos
- Success Story Of Elon Musk
- Top 10 Business Magazine In India
- Top 10 Business Newspaper In India
- Top 10 richest billionaires in the world 2021
- Upcoming English Web Series in 2021
- Top 10 Tourist Places in India, places to visit after lockdown